6.5. Скрипты XILab¶
- Краткое описание языка
- Подсветка синтаксиса
- Дополнительные функции, предоставляемые XILab
- Примеры
- Скрипт-пример работы с битовыми масками
- Скрипт сканирования и записи в файл
- Многоосный скрипт циклического движения
- Одноосный скрипт циклического движения
- Скрипт проверки калибровки домашней позиции
- Скрипт для поиска серийных номеров контроллеров
- Скрипт перемещения и ожидания
- Скрипт случайного сдвига
- Скрипт установки нулевой позиции
- Скрипт для автотестирования
- Тест на пересечение границ
- Тест настройки с замкнутым контуром
- Скрипт дискретного движения
- Экспоненциальное изменение позиции использующие user units
- Шаговый скрипт использующий user units
- Шаговый скрипт
- Тест калибровки домашней позиции сигналу со входа EXTIO
- Скрипт движения по sin
- Скрипт перемещения по сигналу со входа EXTIO. Движение осуществляется в user units
- Вероятные тесты
- Скрипт выполняющий ряд смещений с калибровкой
- Тест на пропуск шагов
- Скрипт тестирования синхронизации
- Скрипт тестирования ошибок синхронизации
Скриптовый язык Xilab реализован с помощью QtScript, он в свою очередь основан на ECMAScript.
ECMAScript — это встраиваемый расширяемый не имеющий средств ввода/вывода язык программирования, используемый в качестве основы для построения других скриптовых языков. Стандартизирован международной организацией ECMA в спецификации ECMA-262.
QtScript (и, соответственно, XILab) использует третью редакцию стандарта ECMAScript.
6.5.1. Краткое описание языка¶
6.5.1.1. Типы данных¶
В ECMAScript поддерживаются девять типов данных. Три из них (Reference, List, и Completion) используются только как промежуточные результаты расчета значений выражений. Оставшиеся шесть типов это:
- Неопределённый,
- Нулевой,
- Логический,
- Строковый,
- Числовой,
- Объектный.
6.5.1.2. Инструкции¶
Наиболее распространенные конструкции языка ECMAScript представлены в таблице ниже:
| Название | Применение | Краткие сведения |
|---|---|---|
| Блок | {[<список инструкций>]} | Несколько инструкций можно объединить в один блок фигурными скобками. |
| Объявление переменной | var <список объявления переменных> | Переменная объявляется с помощью ключевого слова «var». |
| Пустая инструкция | ; | Точка с запятой является пустой инструкцией. Заканчивать строки точкой с запятой не обязательно. |
| Условие | if (<условие>) <инструкция> [ else <инструкция> ] | Условное выполнение можно производить с помощью ключевых слов «if … else». Если условие верно, то выполняется инструкция блока if, в противном случае выполняется инструкция блока else, если он присутствует. |
| Цикл | do <тело цикла> while (<условие>) while (<условие>) <тело цикла> for ([<выражение 1>]; [<условие>]; [<выражение 2>]) <тело цикла> | Цикл можно реализовать несколькими различными способами. Форма «do … while …» выполняет тело цикла как минимум один раз и пока условие верно. Форма «while … do …» выполняет тело цикла пока условие верно. Форма «for …» выполняет выражение до начала (выражение 1), а затем выполняет тело цикла каждый раз после выполнения итеративного выражения (выражение 2) и проверки условия на истинность. |
| Возврат | return [<выражение>] | Прекращает выполнение функции и возвращает выражение как результат. |
| Генерация исключения | throw <выражение> | Генерирует исключение, которое может быть обработано конструкцией try (см.ниже). |
| Блок try | try <блок> catch (<идентификатор>) <блок> try <блок> finally <блок> try <блок> catch (<идентификатор>) <блок> finally <блок> | Используется совместно с исключениями. Конструкция «try … catch … finally» пытается выполнить блок try. Если в этом блоке происходит исключение идентификатор, то выполняется содержимое блока catch. После всего безусловно выполняется блок finally. Один из блоков «catch» и «finally» может отсутствовать. |
6.5.1.3. Объявление переменных¶
Переменные определяются с помощью ключевого слова var. При объявлении переменная помещается в область видимости, соответствующую функции, в которой она объявляется. Если переменная объявляется вне функций, она помещается в глобальную область видимости. Создание переменной происходит при получении управления функцией с её объявлением. Или программой, если переменная глобальна. При создании переменной в ECMAScript она приобретает значение undefined. Если переменная объявлена с инициализацией, инициализация происходит не в момент создания переменной, а при выполнении строки с инструкцией var.
6.5.1.4. Ключевые и зарезервированные слова¶
Следующие слова являются ключевыми в языке и не могут быть использованы как идентификаторы:
break else new var
case finally return void
catch for switch while
continue function this with
default if throw
delete in try
do instanceof typeof
Следующие слова используются как ключевые в предлагаемых расширениях и зарезервированы:
abstract enum int short
boolean export interface static
byte extends long super
char final native synchronized
class float package throws
const goto private transient
debugger implements protected volatile
double import public
6.5.1.5. Функции¶
Функции в ECMAScript являются объектами. Функции, как и любые другие объекты, могут храниться в переменных, объектах и массивах, могут передаваться как аргументы в другие функции и могут возвращаться функциями. Функции, как и любые другие объекты, могут иметь свойства. Существенной специфической чертой функций является то, что они могут быть вызваны.
В тексте программы именованную функцию в ECMAScript обычно определяют следующим способом:
function sum(arg1, arg2) { // a function which takes two parameters
return arg1 + arg2; // and returns their sum
}
6.5.2. Подсветка синтаксиса¶
Шрифт текста в окне скрипта имеет подсветку синтаксиса. Цвета:
| Тип выражения | цвет | пример отображения |
|---|---|---|
| Произвольные функции | фиолетовый | 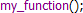 |
| Функции XILab | синий | 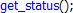 |
| Положительные числа | зеленый | 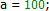 |
| Отрицательные числа | красный | 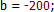 |
| Комментарии | серый | 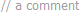 |
| Все остальное | черный | 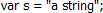 |
Во время выполнения скрипта фон строки с последней выполненной командой меняется на тёмно-серый с частотой обновления 1 раз в 20 мс.
6.5.3. Дополнительные функции, предоставляемые XILab¶
На данной картинке изображены функции, которые XILab предоставляет для использования в скриптах в дополнение к стандартным функциям языка.
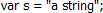
- log(string text [, int loglevel]) - запись в лог XILab
- msleep(int ms) - задержка выполнения скрипта
- new_axis(int serial_number) - создание объекта типа «ось»
- new_file(string filename) - создание объекта типа «файл»
- new_calibration(int A, int Microstep) - создание структуры калибровки для передачи калиброванным функциям
- get_next_serial(int serial) - получение следующего серийного номера
- command_wait_for_stop(int refresh_period) - ожидание остановки движения
- а также все функции библиотеки libximc (см. Руководство по программированию)
Кроме этого, в скриптах определены и доступны для использования все константы протокола обмена. Пример использования.
6.5.3.1. Запись в лог XILab¶
Производится вызовом функции log(string text [, int loglevel] ). Дописывает в лог XiLab строку text. Если передаётся второй параметр loglevel, то сообщение получает соответствующий уровень логгирования и отображается соответствующим цветом.
| Loglevel | Тип |
|---|---|
| 1 | Error |
| 2 | Warning |
| 3 | Info |
Пример:
var x = 5;
log("x = " + x);
Замечание: не рекомендуется вызывать функции интерфейса Xilab (запись в лог) чаще одного раза в 20 мс.
6.5.3.2. Задержка выполнения скрипта¶
Производится вызовом функции msleep(int ms). Скрипт делает паузу в данном месте выполнения длиной ms миллисекунд.
Пример:
msleep(200);
6.5.3.3. Cоздание объекта типа «ось»¶
Многоосевой интерфейс XILab также предоставляет возможность управлять контроллерами посредством скриптов. Отличия состоят в том, что необходимо явно указывать, какому контроллеру посылается команда. Для этого вводится новый тип объекта «ось», который имеет методы, совпадающие по именам с функциями библиотеки . Идентификация происходит по серийному номеру. контроллера.
Пример:
var x = new_axis(123);
x.command_move(50);
В этом примере в первой строке скрипта происходит создание оси с именем переменной x, которая соответствует контроллеру с серийным номером «123». Если такой контроллер не подключен к компьютеру, то скрипт выдаст ошибку выполнения и завершится. Во второй строке оси x подается команда переместиться в координату 50 [шагов].
6.5.3.4. Cоздание объекта типа «фай뻶
Скрипты Xilab имеют возможность чтения из файла и записи в файл. Для этого необходимо создать объект типа файл и работать с ним. Имя файла указывается при создании в конструкторе. Объект имеет следующие функции:
| Тип_возврата Имя_функции | Краткие сведения |
| bool open() | Открывает файл. Файл открывается на чтение-запись, если это возможно; если нет, то только на чтение. |
| void close() | Закрывает файл. |
| Number size() | Возвращает размер файла в байтах. |
| bool seek(Number pos) | Устанавливает текущую позицию в файле в pos байт [1]. |
| bool resize(Number size) | Изменяет размер файла до size байт. Если size меньше текущего размера, то файл обрезается, если больше, то дополняется нулями. |
| bool remove() | Удаляет файл. |
| String read(Number maxsize) | Читает строку из файла, но не более maxsize байт. Данные читаются в кодировке utf-8. |
| Number write(String s, Number maxsize) | Записывает строку в файл, но не более maxsize байт. Данные записываются в кодировке utf-8, символ конца строки пользователь должен записать самостоятельно. Возвращает количество записанных байт, либо -1, если произошла ошибка. |
Все функции работы с файлами, возвращающие значение типа bool, возвращают «true» в случае успеха, в противном случае «false».
Используйте символ «/» как разделитель путей для работы скриптов на всех платформах (Windows/Linux/Mac).
Пример:
var winf = new_file("C:/file.txt"); // An example of file name and path on Windows
var linf = new_file("/home/user/Desktop/file.txt"); // An example of file name and path on Linux
var macf = new_file("/Users/macuser/file.txt"); // An example of file name and path on Mac
var f = winf; // Pick a file name
if (f.open()) { // Try to open the file
f.write( "some text" ); // If successful, then write desired data to the file
f.close(); // Close the file
} else { // If file open failed for some reason
log( "Failed opening file" ); // Log an error
}
6.5.3.5. Cоздание структуры калибровки¶
функция new_calibration(double A, int Microstep) принимает в качестве параметров коэффициент A пересчета из шагов в пользовательские единицы и деление микрошага Microstep (либо полученное ранее вызовом функции get_engine_settings в поле MicrostepMode, либо задаваемое одной из констант MICROSTEP_MODE_) и возвращает структуру типа calibration_t, которую необходимо передать в калиброванные get_/set_* функции для получения/задания величин в пользовательских единицах. Следующие две записи функционально эквивалентны:
// create calibration: type 1
var calb = new_calibration(c1, c2);
// create calibration: type 2
var calb = new Object();
calb.A = c1;
calb.MicrostepMode = c2;
6.5.3.6. Получение следующего серийного номера¶
функция get_next_serial(int serial) принимает в качестве параметра число и возвращает наименьший серийный номер из списка серийных номеров открытых устройств, который больше переданного ей параметра. Если такого серийного номера нет, то возвращается 0. Эта функция удобна для автоматического создания объекта типа «ось» без задания фиксированного серийного номера.
Пример:
var first_serial = get_next_serial(0);
var x = new_axis(first_serial);
var y = new_axis(get_next_serial(first_serial));
В этом примере в первой строке происходит получение первого серийного номера, во второй - создание объекта оси по этому серийному номеру, в третьей - получение следующего серийного номера и создание оси для него.
6.5.3.7. Ожидание остановки движения¶
Функция command_wait_for_stop(int refresh_period) останавливает выполнение скрипта до тех пор, пока контроллер не прекратит движение, то есть, пока флаг MVCMD_RUNNING в члене MvCmdSts структуры, возвращаемой функцией get_status(), не будет снят. Функция скриптов command_wait_for_stop напрямую использует функцию command_wait_for_stop библиотеки libximc и принимает в качестве параметра число, означающее периодичность (в миллисекундах) считывания состояния контроллера.
Эта функция также присутствует как метод объекта типа «ось».
6.5.3.8. Функции библиотеки libximc¶
Функции библиотеки libximc начинающиеся на «get_» считывают из контроллера настройки и возвращают соотвествующую команде структуру данных. Функции библиотеки libximc начинающиеся на «set_» принимают как параметр структуру данных и записывают эти настройки в контроллер. Заполнить структуру данных для set-функций можно двумя способами:
- вызвать соответствующую get-функцию и модифицировать необходимые поля
// set settings: type 1
var m = get_move_settings();
m.Speed = 100;
set_move_settings(m);
- создать объект (Object) и заполнить все его свойства (properties) с именами членов структуры с учетом регистра.
// set settings: type 2
var m = new Object;
m.Speed = 100;
m.uSpeed = 0;
m.Accel = 300;
m.Decel = 500;
m.AntiplaySpeed = 10;
m.uAntiplaySpeed = 0;
set_move_settings(m);
Необходимо помнить, что при использовании первого способа в контроллер посылается дополнительная команда (вызывается не только set-функция, но и get- перед этим), а при использовании второго способа необходимо инициализировать все свойства объекта, соответствующие именам членов структуры. Если в объекте какое-то свойство будет пропущено, то оно будет считаться равным нулю. Если в объекте будет объявлено какое-либо дополнительное свойство, не входящее в структуру данных, то оно будет проигнорировано. Если тип данных какого-либо поля не будет соответствовать типу данных структуры, то будет произведено приведение типов по правилам EcmaScript. Структуры данных для всех команд описаны в главе Описание протокола.
6.5.4. Примеры¶
В этом разделе приведены примеры типичных действий, которые можно выполнять с помощью скриптов XILab.
6.5.4.1. Скрипт-пример работы с битовыми масками¶
/*
* Bit mask example script
*
* Description of the script:
* This script clearly shows how to work with bit masks.
* This script or part of it may be needed when working with any of our other commands that use bit masks. For example, the «set_home_settings» command
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var a = new_axis(get_next_serial(0)); // take first found axis
var gets = a.get_status(); // read status once and reuse it
var gpio = gets.GPIOFlags;
var left = STATE_LEFT_EDGE;
var right = STATE_RIGHT_EDGE;
var mask = left | right;
var result = gpio & mask;
log( to_binary(left) + " = left limit switch flag" );
log( to_binary(right) + " = right limit switch flag" );
log( to_binary(mask) + " = OR operation on flags gives the mask" );
log( to_binary(gpio) + " = gpio state" );
log( to_binary(result) + " = AND operation on state and mask gives result" );
if ( result ) {
log("At least one limit switch is on");
} else {
log("Both limit switches are off");
}
// Binary representation function
function to_binary(i)
{
bits = 32;
x = i >>> 0; // coerce to unsigned in case we need to print negative ints
str = x.toString(2); // the binary representation string
return (repeat("0", bits) + str).slice (-bits); // pad with zeroes and return
}
// String repeat function
function repeat(str, times)
{
var result="";
var pattern=str;
while (times > 0) {
if (times&1) {
result+=pattern;
}
times>>=1;
pattern+=pattern;
}
return result;
}
6.5.4.2. Скрипт сканирования и записи в файл¶
/*
* A script which scans and writes data to the file
*
* Description of the script:
* This script scans and writes the data to a .csv file.
* The script can be useful if you are using the system to scan an area and/or capture frames
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var start = 0; // Starting coordinate in steps
var step = 10; // Shift amount in steps
var end = 100; // Ending coordinate in steps
var speed = 300; // maximum movement speed in steps / second
var accel = 100; // acceleration value in steps / second^2
var decel = 100; // deceleration value in steps / second^2
var delay = 100;
var m = get_move_settings(); // read movement settings from the controller
m.Speed = speed; // set movement speed
m.Accel = accel; // set acceleration
m.Decel = decel; // set deceleration
set_move_settings(m); // write movement settings into the controller
var f = new_file("C:/a.csv"); // Choose a file name and path
f.open(); // Open a file
f.seek( 0 ); // Seek to the beginning of the file
command_move(start); // Move to the starting position
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // Wait until controller stops moving
while (get_status().CurPosition < end) {
f.write( get_status().CurPosition + "," + get_chart_data().Pot + "," + Date.now() + "\n" ); // Get current position, potentiometer value and date and write them to file
command_movr(step); // Move to the next position
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // Wait until controller stops moving
}
f.close(); // Close the file
- пример файла для использования с приведенным выше скриптом
6.5.4.3. Многоосный скрипт циклического движения¶
/*
* Multi axis cyclic movement script
*
* Description of the script:
* Does cyclic movement between two border points with set values of acceleration,
* deceleration and top speed, for all axes found. The script is similar to the "Cyclic"
* button in XILab
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var axes = [];
var number_of_axes = 0;
var last_serial = 0;
while (serial = get_next_serial(last_serial)) // Get next serial number and repeat for each axes
{
axes[number_of_axes] = new_axis(serial);
log("Found axis " + number_of_axes + " with serial number " + serial);
number_of_axes++;
last_serial = serial;
}
for (var i = 0; i < number_of_axes; i++)
{
axis_configure(axes[i]);
}
while (1)
{
for (var i = 0; i < number_of_axes; i++)
{
go_first_border(axes[i]);
go_second_border(axes[i]);
}
msleep(100);
}
function axis_configure(axis)
{
var speed = 1000; // Maximum movement speed in steps / second
var accel = 2000; // Acceleration value in steps / second^2
var decel = 5000; // Deceleration value in steps / second^2
axis.command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
axis.command_zero(); // send ZERO command (sets current position and encoder value to zero)
var m = axis.get_move_settings(); // read movement settings from the controller
m.Speed = speed; // set movement speed
m.Accel = accel; // set acceleration
m.Decel = decel; // set deceleration
axis.set_move_settings(m); // write movement settings into the controller
}
function go_first_border(axis)
{
var first_border = 0; // first border coordinate in steps
var GETS = axis.get_status();
if (!(GETS.MvCmdSts & MVCMD_RUNNING) && (GETS.CurPosition != first_border))
{
axis.command_move(first_border); // move towards one border
}
}
function go_second_border(axis)
{
var second_border = 25000; // second border coordinate in steps
var GETS = axis.get_status();
if (!(GETS.MvCmdSts & MVCMD_RUNNING) && (GETS.CurPosition != second_border))
{
axis.command_move(second_border); // move towards another border
}
}
6.5.4.4. Одноосный скрипт циклического движения¶
/*
* Single axis cyclic movement script
*
* Description of the script:
* Does cyclic movement between two border points with set values of acceleration,
* deceleration and top speed. The script is similar to the "Cyclic" button in XILab
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var first_border = -10; // first border coordinate in mm
var second_border = 10; // second border coordinate in mm
var mm_per_step = 0.005; // steps to distance translation coefficient
var delay = 100; // delay in milliseconds
var calb = new_calibration(mm_per_step, get_engine_settings().MicrostepMode); // create calibration structure
command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
command_zero(); // send ZERO command (sets current position and encoder value to zero)
while (1) { // infinite loop
command_move_calb(first_border, calb); // move towards one border
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // wait until controller stops moving
command_move_calb(second_border, calb); // move towards another border
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // wait until controller stops moving
}
6.5.4.5. Скрипт проверки калибровки домашней позиции¶
/*
* Homing test script
*
* Description of the script:
* This script tests homing function by repeatedly moving to a random position,
* doing quick stop and then homing, for all axes found. The script is similar to the GO
* Home button in XILab
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var axes = [];
var number_of_axes = 0;
var last_serial = 0;
while (serial = get_next_serial(last_serial)) // get next serial number and repeat for each axes.
{
axes[number_of_axes] = new_axis(serial);
log("Found axis " + number_of_axes + " with serial number " + serial);
number_of_axes++;
last_serial = serial;
}
while (1) { // infinite loop
for (var i = 0; i < number_of_axes; i++)
{
homing_test(axes[i]);
}
}
function homing_test(axis)
{
var shift_low = 0; // minimum shift distance in steps
var shift_high = 10000; // maximum shift distance in steps
var speed_low = 100; // minimum movement speed in steps / second
var speed_high = 5000; // maximum movement speed in steps / second
var time_low = 1; // minimum wait time in seconds
var time_high = 10; // maximum wait time in seconds
axis.command_home(); // send HOME command (find home position)
axis.command_wait_for_stop(100); // wait until controller stops moving
var m = axis.get_move_settings(); // read movement settings from the controller
m.Speed = rnd(speed_low, speed_high); // set random speed from a range of speeds between "speed_low" and "speed_high"
axis.set_move_settings(m); // write movement settings into the controller
var shift = rnd(shift_low, shift_high); // pick random shift value from a range of distances between "shift_low" and "shift_high"
if (Math.random() < 0.5) { // pick random direction
shift = -shift;
}
axis.command_movr(shift); // send MOVR command (does a relative shift)
msleep( rnd(time_low*1000, time_high*1000) ); // pause for a random time from a range between "time_low" and "time_high"
axis.command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
}
function rnd(min,max) { // "rnd" is a helper function which uses Math.random() and returns a uniformly distributed integer random value between "min" and "max"
var r = Math.random()*(max-min)+min;
return Math.round(r);
}
6.5.4.6. Скрипт для поиска серийных номеров контроллеров¶
/*
* List axis serials script
*
* Description of the script:
* An example of a script that searches for all the serial numbers of controllers
* and outputs them to the log.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var i = 0; // Declare loop iteration variable
var serial = 0; // Declare serial number variable
var axes = Array(); // Declare axes array
while (true) { // The loop
serial = get_next_serial(serial); // Get next serial
if (serial == 0) // If there are no more controllers then...
break; // ...break out of the loop
var a = new Object(); // Create an object
a.serial = serial; // Assign serial number to its "serial" property
a.handle = new_axis(serial); // Assign new axis object to its "handle" property
axes[i] = a; // Add it to the array
i++; // Increment counter
}
for (var k=0; k < axes.length; k++) { // Iterate through array elements
log ( "Axis with S/N " + axes[k].serial + " is in position " + axes[k].handle.get_status().CurPosition ); // For each element print saved axis serial and call a get_status() function
}
6.5.4.7. Скрипт перемещения и ожидания¶
/*
* Move and wait script
*
* Description of the script:
* The script reads the next coordinate and the delay time from the csv file,
* after which it moves to the specified coordinate with a subsequent delay,
* and so on until the end of reading the entire file.
* The script can be useful if you are using the system to scan an area and/or capture frames
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var axis = new_axis(get_next_serial(0)); // Use first available controller
var x; // A helper variable, represents coordinate
var ms; // A helper variable, represents wait time in milliseconds
var f = new_file("./move_and_sleep.csv"); // Choose a file name and path; this script uses a file from examples in the installation directory
f.open(); // Open a file
while ( str = f.read(4096) ) { // Read file contents string by string, assuming each string is less than 4 KiB long
var ar = str.split(","); // Split the string into substrings with comma as a separator; the result is an array of strings
x = ar[0]; // Variable assignment
ms = ar[1]; // Variable assignment
log( "Moving to coordinate " + x ); // Log the event
axis.command_move(x); // Move to the position
axis.command_wait_for_stop(100); // Wait until the movement is complete
log( "Waiting for " + ms + " ms" ); // Log the event
msleep(ms); // Wait for the specified amount of time
}
log ( "The end." );
f.close(); // Close the file
6.5.4.8. Скрипт случайного сдвига¶
/*
* Random shift script
*
* Description of the script:
* This script does shifts on random offset from a specified range of distances
* with a random speed from a chosen range of speeds.
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var axes = [];
var number_of_axes = 0;
var last_serial = 0;
while (serial = get_next_serial(last_serial)) // get next serial number and repeat for each axes.
{
axes[number_of_axes] = new_axis(serial);
log("Found axis " + number_of_axes + " with serial number " + serial);
number_of_axes++;
last_serial = serial;
}
while (1) { // infinite loop
for (var i = 0; i < number_of_axes; i++)
{
go_to_random_shift(axes[i]);
}
}
function go_to_random_shift(axis)
{
var shift_low = 0; // minimum shift distance in steps
var shift_high = 10000; // maximum shift distance in steps
var speed_low = 100; // minimum movement speed in steps / second
var speed_high = 5000; // maximum movement speed in steps / second
var m = axis.get_move_settings(); // read movement settings from the controller
m.Speed = rnd(speed_low, speed_high); // set random speed from a range of speeds between "speed_low" and "speed_high"
axis.set_move_settings(m); // write movement settings into the controller
var shift = rnd(shift_low, shift_high); // pick random shift value from a range of distances between "shift_low" and "shift_high"
if (Math.random() < 0.5) { // pick random direction
shift = -shift;
}
axis.command_movr(shift); // send MOVR command (does a relative shift)
axis.command_wait_for_stop(100); // wait until controller stops moving
}
function rnd(min,max) { // "rnd" is a helper function which uses Math.random() and returns a uniformly distributed integer random value between "min" and "max"
var r = Math.random()*(max-min)+min;
return Math.round(r);
}
6.5.4.9. Скрипт установки нулевой позиции¶
/*
* Set zero script
*
* Description of the script:
* This script changes "standoff" setting (found on "Home position" page in the XILab "Settings") so that the current position becomes the home position.
* The script is very convenient for calibrating and configuring new stages, as well as for changing the zero position
*
* How to use:
* - manually move your positioner to a desired position
* - launch this script and wait for completion
* As a result your positioner will return to the starting position and all subsequent calls to "homing" function will bring it there.
*
* Note: homing settings are saved into RAM and will be lost when controller is powered down. If you wish to save these settings to non-volatile memory you should either pick "Save settings to flash" on the XILab main Settings page or call "command_save_settings()" at the end of the script.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var axes = [];
var number_of_axes = 0;
var last_serial = 0;
while (serial = get_next_serial(last_serial)) // get next serial number and repeat for each axes.
{
axes[number_of_axes] = new_axis(serial);
log("Found axis " + number_of_axes + " with serial number " + serial);
number_of_axes++;
last_serial = serial;
}
for (var i = 0; i < number_of_axes; i++)
{
set_zero(axes[i]);
}
function set_zero(axis)
{
axis.command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
var h = axis.get_home_settings(); // read homing settings from the controller
h.HomeDelta = 0; // set "HomeDelta" parameter in "home_position" structure to 0
h.uHomeDelta = 0; // set "uHomeDelta" parameter in "home_position" structure to 0
var saved_fast = h.FastHome; // save "FastHome" parameter from "home_position" structure to a variable
var saved_ufast = h.uFastHome; // save "uFastHome" parameter from "home_position" structure to a variable
if (h.HomeFlags & HOME_MV_SEC_EN != 0) // if homing settings have two homing phases turned on
{
h.FastHome = 100; // set "FastHome" parameter in "home_position" structure (first movement speed) to 100 steps/s: this is required to avoid slip at the end of the first phase
h.uFastHome = 0; // set "uFastHome" parameter in "home_position" structure to 0
}
axis.set_home_settings(h); // write homing settings into the controller
var old_pos = axis.get_status().CurPosition; // save whole step part of the initial position into a variable
var old_upos = axis.get_status().uCurPosition; // save microstep part of the initial position into a variable
axis.command_home(); // send HOME command (find home position)
do { msleep(100); } while (axis.get_status().MvCmdSts == (MVCMD_HOME | MVCMD_RUNNING)); // query controller state every 100 ms while movement state is "homing command is being executed"
if (axis.get_status().MvCmdSts != MVCMD_HOME) // if current state is not "homing completed successfully" (MVCMD_RUNNING unset, MVCMD_ERROR unset, last command MVCMD_HOME) then homing was interrupted
{
h.FastHome = saved_fast; // set "FastHome" parameter in "home_position" structure to a saved value
h.uFastHome = saved_ufast; // set "uFastHome" parameter in "home_position" structure to a saved value
axis.set_home_settings(h); // write movement settings into the controller (this restores the initial settings)
throw "Script aborted: homing failed."; // throw an exception and terminate
}
var new_pos = axis.get_status().CurPosition; // read whole part of new position into "new_pos" variable
var new_upos = axis.get_status().uCurPosition; // read microstep part of new position into "new_upos" variable
h.HomeDelta = old_pos-new_pos; // set "HomeDelta" parameter in "home_position" structure to this value
h.uHomeDelta = old_upos-new_upos; // set "uHomeDelta" parameter in "home_position" structure to this value
h.FastHome = saved_fast; // set "FastHome" parameter in "home_position" structure to a saved value
h.uFastHome = saved_ufast; // set "uFastHome" parameter in "home_position" structure to a saved value
axis.set_home_settings(h); // write movement settings into the controller
axis.command_move(old_pos, old_upos); // move to initial position
do { msleep(100); } while (axis.get_status().MvCmdSts == (MVCMD_MOVE | MVCMD_RUNNING)); // query controller state every 100 ms while movement state is "movement command is being executed"
if (axis.get_status().MvCmdSts != MVCMD_MOVE) // if current state is not "movements completed successfully" (MVCMD_RUNNING unset, MVCMD_ERROR unset, last command MVCMD_MOVE) then movement was interrupted
{
throw "Script aborted: return to position failed."; // throw an exception and terminate
}
axis.command_zero(); // send ZERO command (sets current position and encoder value to zero)
}
log("Done."); // log success
6.5.4.10. Скрипт для автотестирования¶
/*
* Autotester script
*
* Description of the script:
* The script tests the controller with a stage using a set of tests.
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
6.5.4.11. Тест на пересечение границ¶
/*
* Border crossing test
*
* Description of the script:
* The script checks the correct operation of the connected external limit switch
*
* How to connect wires?
* You must connect the limit switch to the DSub-15 connector (pins 8 and 9 on the controller connector).
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
const MVCMD_ERROR = 0x40;
const MVCMD_RUNNING = 0x80;
var axis = new_axis(get_next_serial(0));
var m = axis.get_extio_settings();
var s = axis.get_status();
var count_error = 0;
var count_good = 0;
function BorderOff()
{
m.EXTIOSetupFlags = 0x01;
m.EXTIOModeFlags = 0x10;
axis.set_extio_settings(m);
}
function BorderOn()
{
m.EXTIOSetupFlags = 0x01;
m.EXTIOModeFlags = 0x00;
axis.set_extio_settings(m);
}
function BorderCycle()
{
BorderOn();
msleep(50);
BorderOff();
msleep(100);
}
log("You have to connect the common",2);
log("input/output pin on the backplane connector to",2);
log("the 2nd limit switch pin on the stage connector", 2);
log("Also its recommended to load the profile for your stage", 2);
log(">>> Start testing", 3);
while (1)
{
axis.command_left();
msleep(200);
BorderOn();
msleep(200);
s = axis.get_status();
if (s.MvCmdSts & MVCMD_RUNNING)
{
count_error++;
log(">>> ALARM ! Crossing through the limit switch !" ,1);
}
else
{
count_good++;
if (!(count_good % 50))
log(">>> " + count_good + " cycles were done correct, " + count_error + " cycles were done incorrect", 3);
}
BorderOff();
}
6.5.4.12. Тест настройки с замкнутым контуром¶
/*
* Closed loop tuning test
*
* Description of the script:
* The script checks the parameters of a closed loop
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var global_axis;
global_axis = new_axis(get_next_serial(0));
global_axis.command_stop();
const DEBUG = 1;
const MICROSTEPS = 256;
const SKIP_ENCODER_COUNT = 7;
const STORE_COUNT_MICROSTEPS = 19;
const TRUST_INDEX = 15; // Always TRUST_INDEX < STORE_COUNT_MICROSTEPS
/*
* Save and overwrite settings
*/
var SFBS = global_axis.get_feedback_settings(); // Save information about encoder (IPS)
SFBS.FeedbackType = FEEDBACK_NONE; // Overwrite feedback type, because in profile feedback is encoder
var SENG = global_axis.get_engine_settings(); // Save information about engine (nominal current, steps per revolution)
var SENT = global_axis.get_entype_settings(); // Save information about engine type
var SEDS = global_axis.get_edges_settings(); // Save information about edges
/*
* Clear FRAM for synchronization
* real full step with full step of firmware
*/
log("Clearing FRAM", 1);
global_axis.command_clear_fram();
msleep(4000);
/*
* Restore controller settings
*/
global_axis.set_feedback_settings(SFBS);
msleep(100);
global_axis.set_engine_settings(SENG);
msleep(100);
global_axis.set_entype_settings(SENT);
msleep(100);
global_axis.set_edges_settings(SEDS);
msleep(100);
/*
* Prepare and apply move settings
*/
var SMOV = global_axis.get_move_settings();
SMOV.Speed = 0;
SMOV.uSpeed = 16;
global_axis.set_move_settings(SMOV);
msleep(100);
/*
* Going to the full step and waiting 3 seconds for equilibration
*/
global_axis.command_move(0, 0);
msleep(3000);
/*
* Arrays for measurements and structure for GPOS
*/
var MicroStepsToRight = [];
var MicroStepsToLeft = [];
var EncToRight = [];
var EncToLeft = [];
var GPOS;
/*
* Start moving
*/
global_axis.command_right();
/*
* Skipping a some first counts for the stable experiment
*/
for (var i = 0; i < SKIP_ENCODER_COUNT; i++)
{
GPOS = global_axis.get_position();
var EncPos = GPOS.EncPosition;
while (EncPos == GPOS.EncPosition)
{
msleep(40);
GPOS = global_axis.get_position();
}
EncPos = GPOS.EncPosition;
}
/*
* Start measurements
*/
for (var i = 0; i < STORE_COUNT_MICROSTEPS; i++)
{
GPOS = global_axis.get_position();
var EncPos = GPOS.EncPosition;
while (EncPos == GPOS.EncPosition)
{
msleep(40);
GPOS = global_axis.get_position();
}
EncPos = GPOS.EncPosition;
MicroStepsToRight[i] = GPOS.Position * MICROSTEPS + GPOS.uPosition;
EncToRight[i] = GPOS.EncPosition;
}
/*
* Stop moving
*/
global_axis.command_stop();
/*
* Start moving and measurements
*/
global_axis.command_left();
for (var i = 0; i < STORE_COUNT_MICROSTEPS; i++)
{
GPOS = global_axis.get_position();
var EncPos = GPOS.EncPosition;
while (EncPos == GPOS.EncPosition)
{
msleep(40);
GPOS = global_axis.get_position();
}
EncPos = GPOS.EncPosition;
MicroStepsToLeft[STORE_COUNT_MICROSTEPS - 1 - i] = GPOS.Position * MICROSTEPS + GPOS.uPosition;
EncToLeft[STORE_COUNT_MICROSTEPS - 1 - i] = GPOS.EncPosition;
}
/*
* Stop moving
*/
global_axis.command_stop();
/*
* Check all values
*/
for (var i = 0; i < STORE_COUNT_MICROSTEPS; i++)
{
var diffMicrosteps = MicroStepsToRight[i] - MicroStepsToLeft[i];
var diffConts = EncToRight[i] - EncToLeft[i];
if (DEBUG)
{
log(MicroStepsToRight[i] + " - " + MicroStepsToLeft[i] + " = " + diffMicrosteps + " microstep(s)\t" +
EncToRight[i] + " - " + EncToLeft[i] + " = " + diffConts + " count(s)", 3);
}
if (diffConts != 1)
{
log("Script error! Try again", 1);
}
}
var RightB = (MicroStepsToRight[TRUST_INDEX] * EncToRight[0] - MicroStepsToRight[0] * EncToRight[TRUST_INDEX]) / (EncToRight[0] - EncToRight[TRUST_INDEX]);
var LeftB = (MicroStepsToLeft[TRUST_INDEX] * EncToLeft[0] - MicroStepsToLeft[0] * EncToLeft[TRUST_INDEX]) / (EncToLeft[0] - EncToLeft[TRUST_INDEX]);
log("Right counts show B = " + RightB, 2);
log("Left counts show B = " + LeftB, 2);
log("Aver B = " + ((RightB + LeftB) / 2), 3);
6.5.4.13. Скрипт дискретного движения¶
/*
* Discrete motion script
*
* Description of the script:
* The script opens two axes by serial numbers. Moves along the X axis to a certain coordinate. Then it begins to shift discretely along the Y axis, with a programmable pause after each offset.
* The script can be useful if you are using the system to scan an area and/or capture frames
*
* Warning: enter the serial numbers of your axes!
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
// Enter the serial numbers of your axes.
serial_number_x = 14889;
serial_number_y = 14888;
var x = new_axis(serial_number_x);
var y = new_axis(serial_number_y);
// Installing the source data
var x_target_coordinate = 5000; // first border coordinate
var delay = 100; // delay in milliseconds
var y_first_border = 0; // first border coordinate
var y_second_border = 5000; // second border coordinate
var y_step = 100
var y_direct = 1
// Calibration and positioning of the axes to their original positions.
x.command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
x.command_zero(); // send ZERO command (sets current position and encoder value to zero)
y.command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
y.command_zero(); // send ZERO command (sets current position and encoder value to zero)
x.command_move(x_target_coordinate); // move to wards one border
x.command_wait_for_stop(10); // wait until controller stops moving
y.command_move(y_first_border); // move towards one border
y.command_wait_for_stop(10); // wait until controller stops moving
// Movement in discrete samples along one axis from the end to the end
// with a delay after each movement.
while (1) { // infinite loop
// Choosing the direction of travel
if (y.get_position() >= y_second_border)
{
y_direct = -1
}
if (y.get_status().CurPosition <= y_first_border)
{
y_direct = 1
}
// Movement in a given direction
y.command_movr(y_step*y_direct); // move towards another border
y.command_wait_for_stop(10); // wait until controller stops moving
msleep(delay);
}
6.5.4.14. Экспоненциальное изменение позиции использующие user units¶
/*
* Exponential position change in user units script
*
* Description of the script:
* The script performs discrete control of movement according to a certain law of motion. The amplitude and the law of displacement are given. A correction speed is used to maintain the positioning accuracy.
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
// Main characteristics
var time_discre = 10; // Discreteness of movement control(ms)
var end_err = 0.01; // The accuracy of reaching the final coordinate of the movement.
var full_move = 6; // Total movement in mm
// If you change the equation of motion, you will need to change the equation for the correction velocity, since this change is not linear.
var K = 0.4;
var Glob_err = 0;
// Advanced setting.
var mm_per_step = 0.00125; // Distance in gr for 1 completed step.
var calb = new_calibration(mm_per_step, get_engine_settings().MicrostepMode); // create calibration structure
// Setting the starting position.
command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
command_wait_for_stop(10); // wait until controller stops moving
command_zero(); // send ZERO command (sets current position and encoder value to zero)
log("Start:");
// Setting 0 speeds and accelerations.
zero_movesettings();
//
go_position(full_move, time_discre)
// Function for calculating the set speed and acceleration
function set_movesettings(time, corr_speed)
{
// Speed, Accel, Decel setting.
var m = get_move_settings_calb(calb); // read movement settings from the controller
// The equation of speed is equal to the derivative of the equation of motion.
m.Speed = K*Math.exp(K*time/1000 )+ corr_speed;
set_move_settings_calb(m, calb); // write movement settings into the controller
log("Speed = " +m.Speed);
log("corr_speed = " +corr_speed);
}
// Set the initial parameters of motion
function zero_movesettings()
{
var m = get_move_settings_calb(calb); // read movement settings from the controller
m.Speed = 0.1; // set movement speed
set_move_settings_calb(m, calb); // write movement settings into the controller
}
// A function of calculating target coordinates from time
function current_target_coordinate(time)
{
// The equation of motion. The time is set in milliseconds. The position at the initial time is 0.
return (Math.exp(K*time/1000) - 1);
}
// The calculation of the correction speed
function speed_corr(err_pos)
{
Glob_err = Glob_err + err_pos*0.35;
return Glob_err;
}
// The main moving
function go_position(full_time, time_discre)
{
Glob_err = 0;
var end_position = full_move;
// Setting the movement to the desired coordinate.
command_move_calb(end_position, calb);
// Pause before starting to move, to turn on the power button.
msleep(300);
var mas = 1;
var basetime = new Date();
var curr_time = new Date();
var err_pos = 0;
var pos = 0;
var pos1 = 0;
var i = time_discre;
do {
// If you do not need position feedback, you can instead speed_corr(err_pos) write 0
set_movesettings(i+1, speed_corr(err_pos));
// Waiting for the end of a discrete time interval
do {
curr_time = new Date - basetime;
msleep(1);
}
while ((curr_time) < i); //
// Reading the actual and calculating the planned coordinate if used.
pos = get_position_calb(calb).Position;
pos1 = current_target_coordinate(i);
// Calculation of the position error.
err_pos = (pos1 - pos);
log("time = " + i);
log("err_pos = " + err_pos);
i = i + time_discre
}
while (Math.abs(pos - end_position) > end_err); // Completion when the end of the movement is reached with the specified accuracy.
}
6.5.4.15. Шаговый скрипт использующий user units¶
/*
* For calb step script
*
* Description of the script:
* In the script, the user units are configured, after which there is a departure to the leftmost position and then a certain number of shifts occur until the right position is reached. Each position is recorded in a .csv file.
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
command_home(); // send HOME command (find home position)
command_wait_for_stop(100);
command_zero();
command_wait_for_stop(100);
// Setting the value to convert to user unit
var mm_per_step = 0.00125; // steps to distance translation coefficient
var calb = new_calibration(mm_per_step, get_engine_settings().MicrostepMode); // create calibration structure
// Setting boundaries and movement step
// Boundaries can be set manually or taken from limit constraints
var edge = get_edges_settings_calb(calb);
var first_border = edge.LeftBorder; //0;
var second_board = edge.RightBorder;//23;
var shift = 5;//step move;
var delay = 2000;// The delay of movement
var f = new_file("file.csv"); // Choose a file name and path
f.open(); // Open a file
f.resize(0);
f.seek( 0 ); // Seek to the beginning of the file
command_move_calb(first_border, calb); // Move to the starting position
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // Wait until controller stops moving
var i = 1;
var time = 0;
var step = (second_board - first_border)/shift;
f.write(0+ "," + get_status().CurPosition + "," + get_status().uCurPosition+ "," + "\n" ); // Get current position, potentiometer value and date and write them to file
do {
time = i*delay;
command_movr_calb(shift, calb); // Move to the next position
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // Wait until controller stops moving
f.write(time + "," + get_position_calb(calb).Position + "," + get_position_calb(calb).EncPosition+ "," + "\n" ); // Get current position, potentiometer value and date and write them to file
i = i+1;
} while ( get_position_calb(calb).Position+shift < second_board )
f.close(); // Close the file
6.5.4.16. Шаговый скрипт¶
/*
* Step script
*
* Description of the script:
* In the script, there is a departure to the leftmost position and then a certain number of shifts occur until the right position is reached. Each position is recorded in a .csv file.
*
* Note: The script is similar to the "for_calb_step" script, only in this script the offset occurs at the step mode
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
command_home(); // send HOME command (find home position)
command_wait_for_stop(100);
command_zero();
command_wait_for_stop(100);
var edge = get_edges_settings();
var first_border = edge.LeftBorder;
var second_board = edge.RightBorder;
var count = 10;
var f = new_file("E:/a.csv"); // Choose a file name and path
f.open(); // Open a file
f.seek( 0 ); // Seek to the beginning of the file
var delay = 2000;
command_move(first_border); // Move to the starting position
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // Wait until controller stops moving
var i = 1;
var time = 0;
var shift = 6;
var step = (second_board - first_border)/shift;
f.write(0+ "," + get_status().CurPosition + "," + get_status().uCurPosition+ "," + "\n" ); // Get current position, potentiometer value and date and write them to file
do {
time = i*delay;
command_movr(step, 0); // Move to the next position
command_wait_for_stop(delay); // Wait until controller stops moving
f.write(time + "," + get_status().CurPosition + "," + get_status().uCurPosition+ "," + "\n" ); // Get current position, potentiometer value and date and write them to file
i = i+1;
} while (i < shift )
f.close(); // Close the file
6.5.4.17. Тест калибровки домашней позиции сигналу со входа EXTIO¶
/*
* Homing test with extio
*
* Description of the script:
* The script starts calibration when a signal is received from a general purpose digital input/output (extio)
*
* How to connect wires?
* You must connect to the HDB-26 connector (pin 25 on the controller).
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
const MVCMD_ERROR = 0x40;
const MVCMD_RUNNING = 0x80;
var axis = new_axis(get_next_serial(0));
var m = axis.get_extio_settings();
var s = axis.get_status();
var count_error = 0;
var count_good = 0;
function BorderOff()
{
m.EXTIOSetupFlags = 0x01;
m.EXTIOModeFlags = 0x10;
axis.set_extio_settings(m);
}
function BorderOn()
{
m.EXTIOSetupFlags = 0x01;
m.EXTIOModeFlags = 0x00;
axis.set_extio_settings(m);
}
function BorderCycle()
{
BorderOn();
msleep(50);
BorderOff();
msleep(2500);
}
log(">>> Start testing", 3);
while (1)
{
axis.command_home();
msleep(1500);
BorderCycle();
BorderCycle();
command_wait_for_stop(100);
s = axis.get_status();
if (s.MvCmdSts & MVCMD_ERROR)
{
count_error++;
log(">>> Alarm! Homing broken", 1);
}
else
{
count_good++;
if (!(count_good % 50))
log(">>> " + count_good + " cycles were done correct, " + count_error + " cycles were done incorrect", 3);
}
}
6.5.4.18. Скрипт движения по sin¶
/*
* Motion by sin function
*
* Description of the script:
* A script for moving with a change in speed according to the trigonometric law.
* The script can be useful for precise positioning of a laser or motorized mirror
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var delay = 100;
/* Definition of delta and initial phase*/
var df = 0.05;
var f = 0;
/* Definition of package */
var GETS = new Object();
// Initial installations
var move_set = get_move_settings();
var speed = 3000;
var amplitude = 1000;
var nomber = 100;
var time = 1000;
var pos = 0;
var Pi = 3.1415;
df = Pi/nomber;
command_zero();
var pos_read = new Object();
while (1)
{
pos_read = get_position();
// Movement to a point with an increase in the velocity amplitude
for (i = 1; i <= nomber-1; i++)
{
f = df*i;
move_set.Speed = speed * Math.sin(f);
pos = amplitude*i /nomber;
set_move_settings(move_set);
command_move(pos);
while (Math.abs(pos_read.Position - pos)>move_set.Speed/10)
{
pos_read = get_position();
}
}
// Movement to a point with a decrease in the velocity amplitude
for (i = nomber-1; i >= 1; i--)
{
f = df*i;
move_set.Speed = speed * Math.sin(f);
pos = amplitude*i /nomber;
set_move_settings(move_set);
command_move(pos);
while (Math.abs(pos_read.Position - pos)>move_set.Speed/10)
{
pos_read = get_position();
}
}
msleep(1000);
}
6.5.4.19. Скрипт перемещения по сигналу со входа EXTIO. Движение осуществляется в user units¶
/*
* Move EXTIO calb script
*
* Description of the script:
* The script moves to one of the 2 specified points, depending on the state of the EXTIO input. The movement is carried out in user units.
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
// Main characteristics
var time_discre = 10; // Discreteness of movement control(ms)
var nomspeed = 5;
var end_err = 0.015;
var low_position = 0; // Move to position for low EXTIO
var high_position = 180; // Move to position for high EXTIO
// Advanced setting.
var gr_per_step = 0.015; // Distance in gr for 1 completed step.
var calb = new_calibration(gr_per_step, get_engine_settings().MicrostepMode); // create calibration structure
// Setting the starting position.
command_stop(); // send STOP command (does immediate stop)
command_wait_for_stop(10); // wait until controller stops moving
command_home();
command_zero(); // send ZERO command (sets current position and encoder value to zero)
log("Start:");
// Setting 0 speeds and accelerations.
movesettings();
extiosettings();
//
go_position(time_discre)
function extiosettings()
{
var extsettings = get_extio_settings();
extsettings.EXTIOSetupFlags = 0x00;
extsettings.EXTIOModeFlags = 0x00;
set_extio_settings(extsettings);
}
// Set the initial parameters of motion
function movesettings()
{
var m = get_move_settings_calb(calb); // read movement settings from the controller
m.Speed = nomspeed; // set movement speed
set_move_settings_calb(m, calb); // write movement settings into the controller
}
// The main moving
function go_position(time_discre)
{
var oldstate = 0;
var maskstate = 32;
// Setting the movement to the desired coordinate.
command_move_calb(low_position, calb);
// Pause before starting to move, to turn on the power button.
msleep(300);
while(1) {
//
var status = get_status_calb(calb);
if ((status.GPIOFlags & maskstate) != oldstate)
{
log(status.GPIOFlags);
if (oldstate)
command_move_calb(high_position, calb);
else
command_move_calb(low_position, calb);
oldstate = status.GPIOFlags & maskstate;
}
// Waiting for the end of a discrete time interval
msleep(time_discre);
}
}
6.5.4.20. Вероятные тесты¶
/*
* Probabilistic tests
*
* Description of the script:
* The script runs a set of repeatable tests a certain number of times and is expected to fail.
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
6.5.4.21. Скрипт выполняющий ряд смещений с калибровкой¶
/*
* Several shifts with calibration script
*
* Description of the script:
* This program makes shifts given number of times to the specified distance, and stands the appointed time after every shift. First it goes left, then it returns back to the origin and repeats all movements to right.
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
const LEFT = -1;
const RIGHT = 1;
var axes = [];
var number_of_axes = 0;
var last_serial = 0;
while (serial = get_next_serial(last_serial)) // get next serial number and repeat for each axes.
{
axes[number_of_axes] = new_axis(serial);
log("Found axis " + number_of_axes + " with serial number " + serial);
number_of_axes++;
last_serial = serial;
}
// Start the main function for all avaliable axes
for (var i = 0; i < number_of_axes; i++)
{
main(axes[i]);
}
function main(axis)
{
axis.command_move(0,0); // Go back to the origin.
msleep(500);
/* Creating and filling the calibration structure for specifying distances in um */
var calibration = new Object;
calibration.A = 5; // 1 step correspond to 5 um for 8MT50-100BS1
calibration.MicrostepMode = axis.get_engine_settings().MicrostepMode; // Get MicrostepMode from controller settings
/*******************************************************/
/* Main cycle */
var N = 10; // Number of shifts
var stand_time = 3000; // Stand time in ms
var shift = 10; // Distance of shift in um
MakeShifts(axis, LEFT, shift, N, stand_time, calibration); // Make 10 shifts to the left
MakeShifts(axis, RIGHT, shift, N, stand_time, calibration); // Make 10 shifts to the right
MakeShifts(axis, RIGHT, shift, N, stand_time, calibration); // Make 10 shifts to the right again
MakeShifts(axis, LEFT, shift, N, stand_time, calibration); // Make 10 shifts to the left
}
function MakeShifts(axis, Direction, ShiftDistance, ShiftsQuantity, StandTime, Calibration)
{
/**
This function makes shifts which number is specified by ShiftQuantity and length is specified by ShiftDistance. After every shift it stands StandTime miliseconds. Calibration parameter is a structure for convertation between steps and micrometers.
*/
for (var i = 0; i < ShiftsQuantity; i++)
{
axis.command_movr_calb(Direction*ShiftDistance, Calibration);
axis.command_wait_for_stop(100);
msleep(StandTime);
}
}
6.5.4.22. Тест на пропуск шагов¶
/*
* Steps loss test
*
* Description of the script:
* The script was written to check for skipping steps
* It can be useful for diagnosing problematic stages
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
function abs(x)
{
return ((x > 0) ? x : -x);
}
/*
* Set home settings
*/
var SHOM = get_home_settings()
SHOM.FastHome = 500;
SHOM.uFastHome = 0;
SHOM.SlowHome = 20;
SHOM.uSlowHome = 0;
SHOM.HomeDelta = 300;
SHOM.uHomeDelta = 0;
SHOM.HomeFlags = HOME_STOP_FIRST_LIM;
set_home_settings(SHOM);
/*
* Check for encoder
*/
var encoder = 1
command_zero()
var first = get_status().EncPosition
command_movr(100)
command_wait_for_stop(300)
var second = get_status().EncPosition
if(abs(second - first) < 2)
{
encoder = 0
log("It seems like here are no encoder", 2)
}
command_home();
command_wait_for_stop(300);
command_zero();
msleep(200);
// Store old move settings
var MOV = get_move_settings();
// Set fast speed and accel\decel
var MOV2 =get_move_settings();
MOV2.Speed = MOV.Speed * 2;
MOV2.Accel = MOV.Accel * 2;
MOV2.Decel = MOV.Decel * 2;
for(var i=0; i < 1; i++) // Set default settings first
{
set_move_settings(MOV2);
// Move long...
command_move(20000);
command_wait_for_stop(300);
// Set prev settings back
set_move_settings(MOV);
// Move back
command_move(0);
command_wait_for_stop(300);
}
if (encoder > 0)
{
var lost = get_status().EncPosition
if (abs(lost) > 1)
{
log("Lost " + lost + " pulses", 1)
}
else
{
log("All is OK");
}
}
else
{
log("Do final homing...")
command_home()
command_wait_for_stop(300)
var lost = get_status().CurPosition
if (abs(lost) > 2)
{
log("Lost " + lost + " steps", 1)
}
else
{
log("All is OK");
}
}
6.5.4.23. Скрипт тестирования синхронизации¶
/*
* Sync test script
*
* Description of the script:
* The script is written to demonstrate the work of synchronization, and also checks its operability
*
* For test you must short special pins on the controller. Pin 5 (sync in) and pin 6 (sync out). See https://doc.xisupport.com/en/8smc5-usb/8SMCn-USB/Technical_specification/Appearance_and_connectors/One_axis_system.html
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
const dX = 4.5;
const dot_num = 5;
const micro2mili = 1000;
var ASIA = [];
for (var i = 0; i < dot_num; i++)
ASIA[i] = new Object();
var calb = new_calibration(1, MICROSTEP_MODE_FRAC_256);
function abs(x)
{
return (x > 0) ? x : -x;
}
function set_default()
{
// SSNI settings
var SSNI = get_sync_in_settings_calb(calb);
SSNI.SyncInFlags = SYNCIN_ENABLED | SYNCIN_GOTOPOSITION;
set_sync_in_settings_calb(SSNI, calb);
// SSNO settings
var SSNO = get_sync_out_settings(calb);
SSNO.SyncOutFlags = SYNCOUT_ENABLED;
SSNO.Accuracy = 0.5;
set_sync_out_settings(SSNO, calb);
// SMOV settings
var SMOV = get_move_settings_calb(calb);
SMOV.Speed = 1000;
SMOV.Accel = 500;
SMOV.Decel = 1000;
SMOV.AntiplaySpeed = 50;
set_move_settings_calb(SMOV, calb);
// SENG settings
var SENG = get_engine_settings();
SENG.NomSpeed = 5000;
SENG.EngineFlags = ENGINE_ACCEL_ON | ENGINE_LIMIT_VOLT | ENGINE_LIMIT_CURR;
SENG.Antiplay = 50;
SENG.MicrostepMode = MICROSTEP_MODE_FRAC_256;
SENG.StepsPerRev = 200;
set_engine_settings(SENG);
}
function send_all_asia()
{
for (var i = 0; i < dot_num; i++)
command_add_sync_in_action_calb(ASIA[i], calb);
}
function check_all_asia()
{
var GETS;
for (var i = 0; i < dot_num; i++)
{
log("> Checking movement ASIA[" + i + "]", 3);
msleep(ASIA[i].Time / micro2mili);
GETS = get_status_calb(calb);
if (abs(GETS.CurPosition - ASIA[i].Position) < dX)
log(">>> OK! GETS.CurSpeed = " + GETS.CurSpeed, 3);
else
log(">>> Error! GETS.CurPosition = " + GETS.CurPosition + ", ASIA[" + i + "].Position = " + ASIA[i].Position, 1);
}
}
function test1()
{
ASIA[0].Position = 22.5;
ASIA[0].Time = 300000;
ASIA[1].Position = 45.0;
ASIA[1].Time = 300000;
ASIA[2].Position = 32.5;
ASIA[2].Time =300000;
ASIA[3].Position = 10;
ASIA[3].Time = 300000;
ASIA[4].Position = -11.5;
ASIA[4].Time = 300000;
}
function test2()
{
ASIA[0].Position = -22.5;
ASIA[0].Time = 300000;
ASIA[1].Position = -45.0;
ASIA[1].Time = 300000;
ASIA[2].Position = -32.5;
ASIA[2].Time =300000;
ASIA[3].Position = -10;
ASIA[3].Time = 300000;
ASIA[4].Position = 11.5;
ASIA[4].Time = 300000;
}
function test3()
{
ASIA[0].Position = -6;
ASIA[0].Time = 300000;
ASIA[1].Position = 6;
ASIA[1].Time = 300000;
ASIA[2].Position = -6;
ASIA[2].Time =300000;
ASIA[3].Position = 6;
ASIA[3].Time = 300000;
ASIA[4].Position = -6;
ASIA[4].Time = 300000;
}
command_zero();
set_default();
log(">>> Function test1() started", 3)
test1();
send_all_asia();
check_all_asia();
msleep(500);
command_zero();
set_default();
log(">>> Function test2() started", 3)
test2();
send_all_asia();
check_all_asia();
msleep(500);
command_zero();
set_default();
log(">>> Function test3() started", 3)
test3();
send_all_asia();
check_all_asia();
msleep(500);
6.5.4.24. Скрипт тестирования ошибок синхронизации¶
/*
* Sync bug test script
*
* Description of the script:
* This script does synchronization test to find sync bug in firmware 3.9.9, 3.8.7, 3.9.10.
* This test only for hardware from ver. 2.2.0 to ver. 2.2.4.
* To begin the test, the first what you need to do is connect synchronization pin 15 to pin 16 on CN1 jack.
* The scripts automatically set all necessary settings for test, and automatically beginning the test.
* As a result you will see a log message with current position of motor and text OK! (green text) or ERROR! (red text).
*
* Note: This is a rather difficult script to learn, since it uses a large number of commands and structures.
*
* To run the script, upload it to the XILab software
*/
var axes = [];
var number_of_axes = 0;
var last_serial = 0;
while (serial = get_next_serial(last_serial)) // get next serial number and repeat for each axes.
{
axes[number_of_axes] = new_axis(serial);
number_of_axes++;
last_serial = serial;
log("Found axis " + number_of_axes + " with serial number " + serial);
}
// SSNI settings
var SSNI = get_sync_in_settings;
SSNI.SyncInFlags = SYNCIN_ENABLED | SYNCIN_GOTOPOSITION; //set flags for synchronization in for enabled and absolute position
SSNI.ClutterTime = 4;// set sync in Clutter Time
SSNI.Position = 0;// set sync in absolute position
SSNI.Speed = 500;// set sync in speed
set_sync_in_settings(SSNI);// set synchronization in settings
// GSNO settings
var GSNO = get_sync_out_settings;
GSNO.SyncOutFlags = SYNCOUT_ENABLED | SYNCOUT_ONPERIOD; // set flags for synchronization out for enabled out and period
GSNO.SyncOutPeriod = 200;// set sync out period
GSNO.SyncOutPulseSteps = 2000;// set sync out Pusle width
set_sync_out_settings(GSNO); // set synchronization out settings
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) // testing cycle
{
GETS = get_status();// get information about device
command_movr(201, 0); // shifting position for 201 steps
command_wait_for_stop(100); // Wait until the movement is complete
if (GETS.CurPosition != 0)// get device current position and compare it with 0
{
log(">>> Error! GETS.CurPosition = " + GETS.CurPosition, 1);// log ERROR, bug is exist
}
else
{
log(">>> OK! GETS.CurPosition = " + GETS.CurPosition, 3); // log OK, bug does not exist
}
}
| [1] | Выйти из файла: если позиция находится за пределами файла, то seek () не должен немедленно расширять файл. Если запись выполняется в этой позиции, файл должен быть расширен. Содержимое файла между предыдущим концом файла и новыми записанными данными НЕ УКАЗАНО и варьируется между платформами и файловыми системами. |